HUMAN EYE (FOR NEET, SSC, UPSC)
Human beings possess a pair of eye. These are the organ of sight. They act as an important sensory organ.
DESCRIPTION OF HUMAN EYE
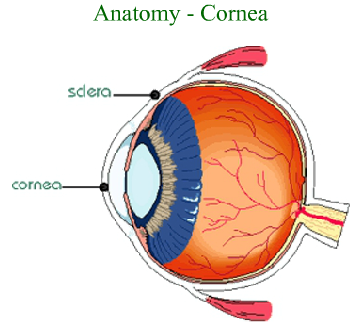
Light rays enter the dark center of the eye, the pupil. The conjunctiva is a mucous membrane that lines the eye lids and coats the anterior portion of the eyeball over the white of the eye. The conjunctiva is clear and colorless except when the blood vessels are dilated. Dust or smoke may cause the blood vessels to dilate and gives the reddish appearance.
The cornea is a fibrous, transparent tissue that extends over the pupil. The function of cornea is to bend, refract the light rays, so that they are focused properly on the sensory receptor cells in the posterior region of the eye. The cornea is avascular region but it receives nourishment from the blood vessels near its junction with the white of the eye, sclera. The sclera is tough, fibrous, supportive, connective tissue that extends from the cornea in the anterior surface of the eyeball to the optic nerve in the back of the eye.

CHOROID AND IRIS
The choroid is a dark brown membrane inside the sclera. It contains many blood vessels that supply nutrients to the eye. The choroid is continuous with the pigment containing region, iris and the ciliary body on the anterior surface of the eye.
Iris gives color to our eyes and surrounds the pupil. Muscles of the iris constricts the pupil in the bright light and dilate the pupil in the dim light, thereby, regulating the amount of light entering the eye.

CILIARY BODY
The ciliary body, on each side of the lens, contains muscles that can adjust the shape and thickness of the lens. These changes in the shape of the lens aid in the refraction of light rays. The lens is thickened and flattened by the muscles of the ciliary body. This refractive power of the lens is known as accommodation.
Besides regulating the shape of the lens, the ciliary body also secretes a fluid called the aqueous humor, which flows through the posterior chamber and the anterior chamber of the eye. Another cavity of the eye is called as the vitreous chamber, which is a large region behind the lens filled with soft, jelly-like material, the vitreous humor. Its function is to maintain the shape of the eyeball.
RETINA
The retina is a thin, delicate and sensitive nerve layer of the eye. As light energy, in the form of waves, travels through the eye, it is refracted, so that it focuses on sensitive receptor cells of the retina called the rods and the cones. The cone functions in the bright light and are helpful in the color vision. Rods functions in the dim light and are helpful in the peripheral vision.
The region in the eye where the optic nerve meets the retina is called as the optical disk. The optic disk is also known as the blind spot. The macula is a small, oval, yellowish area to the side of the optical disk. It contains a central depression called as the fovea centralis composed largely of the cones and is the sharpest region in the human eye. If a portion of fovea or macula is degenerated then vision is affected.

Q.1. The white region of human eye is known as:
- Fovea
- Macula
- Sclera
- Cornea
Ans. c
Q.2. Which region of the human eye is donated and transplanted:
- Cornea
- Conjunctiva
- Sclera
- Retina
Ans. a
Q.3. Which region of the human eye contains photo receptor cells:
- Retina
- Cornea
- Blind spot
- Conjunctiva
Ans. a
Q.4. Which cells help in the night vision:
- Rod
- Cones
- Iris
- Pupil
Ans. a
Q.5. Which cells help in the bright vision:
- Rod
- Cones
- Iris
- Pupil
Ans. b
Q.6. The region that gives color to the human eye:
- Pupil
- Iris
- Rods
- Cones
Ans. b
Q.7. Infection in the conjunctiva causes:
- Blindness
- Myopia
- Hypermetropia
- Conjunctivitis
 IT2EDU Empowering Education Through Technology
IT2EDU Empowering Education Through Technology