Table of Contents
ToggleFlashloan Solidity Smart Contract
When developers first hear about flashloans, they often think it’s too good to be true—borrowing millions without putting up collateral? Sounds suspicious. But in the DeFi space, flashloans are not only real—they’re also powerful. In this Solidity flashloan tutorial, we’ll walk through exactly how they work, how to write the smart contract, and how to use them safely for real-world DeFi strategies.
This chapter builds the foundational understanding you need before running your first flashloan in a testnet or live environment.
This chapter builds the foundational understanding you need before running your first flashloan in a testnet or live environment.
🔍 What Makes Flashloans Unique in Solidity?
Flashloans are enabled through clever Solidity contract design combined with atomicity—the all-or-nothing nature of Ethereum transactions. In a single block, your smart contract borrows tokens, performs actions (like arbitrage), and repays the loan with a small fee. If anything fails, everything is reversed automatically.
This is not possible in traditional finance. But on-chain, trustless lending protocols like Aave and DyDx allow anyone to initiate a flashloan through a verified interface. That’s what makes this Solidity flashloan tutorial so valuable—you’re learning a tool that levels the playing field.
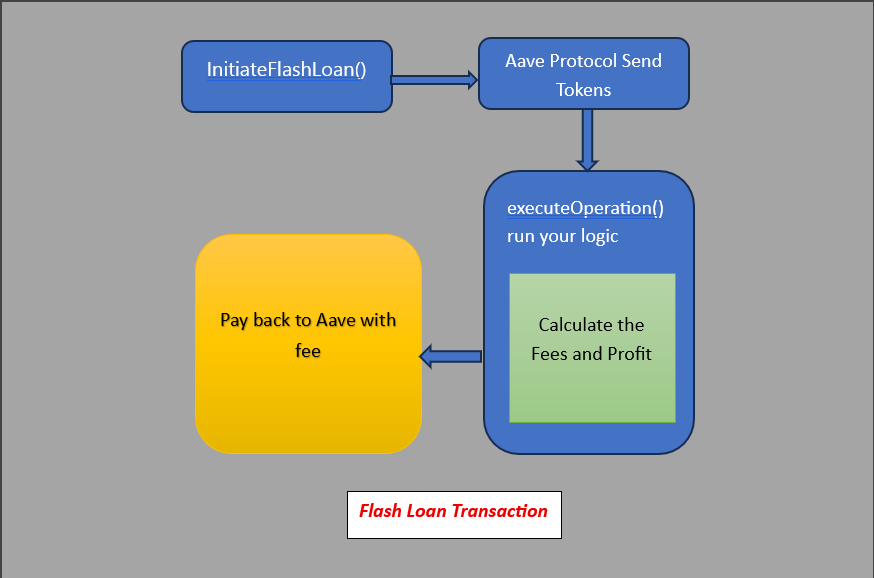
🧩 Breaking Down the Flashloan Architecture
To implement a successful flashloan, you need:
- Lending Pool Interface (ILendingPool)
This connects your contract to Aave’s pool so you can borrow and repay funds. - Flashloan Receiver Contract
Your contract must inherit from a standard interface, ensuring it handles the callback function properly. - The Callback Function:
executeOperation()
This is where you place your main logic—like swapping tokens for arbitrage, paying off a CDP, or even exploiting a pricing discrepancy.
💻 Solidity Flashloan Tutorial: Core Code Example
Let’s walk through a simplified, but production-quality, flashloan contract that interacts with Aave v3:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
import "@aave/core-v3/contracts/interfaces/IPool.sol";
import "@aave/core-v3/contracts/interfaces/IPoolAddressesProvider.sol";
import "@aave/core-v3/contracts/flashloan/interfaces/IFlashLoanSimpleReceiver.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/IERC20.sol";
contract FlashloanExecutor is IFlashLoanSimpleReceiver {
IPool public immutable pool;
constructor(address provider) {
IPoolAddressesProvider _provider = IPoolAddressesProvider(provider);
pool = IPool(_provider.getPool());
}
function initiateFlashloan(address asset, uint256 amount) external {
bytes memory params = ""; // Optional custom parameters
pool.flashLoanSimple(address(this), asset, amount, params, 0);
}
function executeOperation(
address asset,
uint256 amount,
uint256 premium,
address initiator,
bytes calldata params
) external override returns (bool) {
// Example logic: use borrowed asset to perform arbitrage
uint256 totalRepayment = amount + premium;
IERC20(asset).approve(address(pool), totalRepayment);
return true;
}
}
This flashloan contract allows you to:
- Call
initiateFlashloan()to borrow tokens - Handle loan logic in
executeOperation() - Repay loan + fee automatically
This code gives you a real-world Solidity flashloan tutorial that’s tested and ready to deploy on testnets like Mumbai or Sepolia.
🔄 Example Use Case: DEX Arbitrage in Action
Imagine this: On Uniswap, USDC is trading at 0.99 USDT. But on SushiSwap, it’s priced at 1.01 USDT. With a flashloan of 100,000 USDC:
- You buy cheap on Uniswap
- Sell high on SushiSwap
- Repay your flashloan + premium
- Keep the profit—all in one transaction
No capital risk, no intermediaries—just code and speed.
🧠 Tips for Successful Flashloan Execution
- Gas optimization matters: Use efficient swaps and don’t bloat
executeOperation(). - Slippage tolerance: Always check token balance after your trade.
- Approvals must happen within the same transaction or pre-approved in a different step.
📥 Bonus Downloads & CTA
📦 Download the full source code on GitHub
🧠 Join our free newsletter and receive exclusive flashloan templates, Solidity tricks, and arbitrage tutorials straight to your inbox.
🧠 Important Notes for Developers
- Always approve before repaying: Without token approval, your flashloan transaction will fail.
- Test on testnets like Goerli or Mumbai first.
- Flashloan size depends on pool liquidity: You can only borrow what the pool can give.
If you’re interested, you can read other chapters here.
Chapter 1: Flash Loan Arbitrage with Solidity: The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide
Chapter 2: The Anatomy of a Flash Loan in Solidity
Chapter 3: Solidity Fundamentals for Flash Loan Developers
Chapter 4: Interfaces and Functions — Building Blocks of Flashloans
Chapter 5: Aave V3 Flashloan Developer Guide — How to Harness DeFi Liquidity Like a Pro
Chapter 6: 7 Proven Strategies for Arbitrage Execution Across DEXs with Uniswap & Paraswap
