Hey guys, some times we received a forwarded message like you will get free recharge or discount coupons if you forward this message to 10 members. But we are not sure weather this message is genuine or not or about message authenticity. To determine if a forwarded message is genuine or fake, we need a specific dataset or criteria to evaluate the message’s authenticity. It is a general approach using natural language processing (NLP) techniques. Please note that this approach may not be foolproof and should be customized based on your specific requirements. To address this issue, we can leverage Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to create a simple Python code that helps evaluate the authenticity of forwarded messages. Please note that while this approach is a valuable starting point, it may require customization based on your specific needs.
The Below is the simple python code to determine the received message is fake or genuine to check Message Authenticity.
To work with below code need to install the python package nltk (Natural language tool kit package).
To install nltk execute the below code in cmd.
C:\Users\DELL>pip install nltk
import nltk
from nltk.sentiment import SentimentIntensityAnalyzer
# Load the NLTK sentiment analyzer
nltk.download('vader_lexicon')
sia = SentimentIntensityAnalyzer()
# Function to determine the authenticity of a forwarded message
def check_message_authenticity(message):
# Preprocess the message (e.g., remove stopwords, punctuation, convert to lowercase, etc.)
# Implement your own preprocessing logic here
# Analyze the sentiment of the message
sentiment_score = sia.polarity_scores(message)
# Define a threshold for sentiment polarity to assess authenticity
threshold = 0.5
# Compare the sentiment score with the threshold
if sentiment_score['compound'] >= threshold:
return "Genuine"
else:
return "Fake"
# Example usage
forwarded_message = "Forward this message to 10 Group your telecom provide gives you 1000 talktime!!! Hurry up i already got"
result = check_message_authenticity(forwarded_message)
print(forwarded_message,"--is",result)
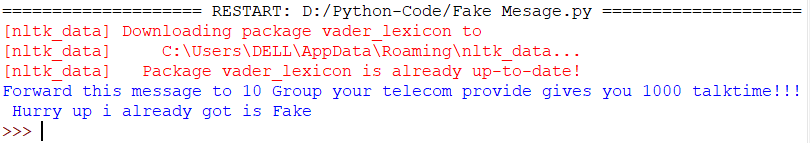
Output of the following is :
==================== RESTART: D:/Python-Code/Fake Mesage.py ====================
[nltk_data] Downloading package vader_lexicon to
[nltk_data] C:\Users\DELL\AppData\Roaming\nltk_data…
[nltk_data] Package vader_lexicon is already up-to-date!
Forward this message to 10 Group your telecom provide gives you 1000 talktime!!! Hurry up i already got is Fake
In this code example, we utilize the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) library and its SentimentIntensityAnalyzer module. Here’s a breakdown of the code:
Understanding the Code for message authenticity
In this code example, we employ the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) library and its SentimentIntensityAnalyzer module to assess message authenticity. Here’s a breakdown of the code:
- Imports: We import the necessary modules, including
nltkfor NLP operations and SentimentIntensityAnalyzer for sentiment analysis. - Downloading Resources: We download the essential NLTK resource, ‘vader_lexicon,’ which is utilized by the sentiment analyzer.
- Message Authenticity Function: We define the check_message_authenticity function. This function takes a message as input and returns whether it is genuine or fake.
- Preprocessing: Inside the function, you can implement your own preprocessing logic based on your requirements. This may involve removing stopwords, punctuation, converting to lowercase, and other text normalization techniques.
- Sentiment Analysis: We utilize the SentimentIntensityAnalyzer to compute the sentiment score of the preprocessed message.
- Threshold Setting: We establish a threshold (e.g., 0.5) to determine whether the sentiment polarity indicates a genuine or fake message. You can adjust this threshold to align with your evaluation criteria.
- Result Display: The sentiment score is compared with the threshold, and the function returns “Genuine” if the sentiment score is above or equal to the threshold, and “Fake” otherwise.
- Example Usage: We demonstrate how to use the code by passing a forwarded message to the check_message_authenticity function and printing the result.
Keep in mind that while this code provides a foundational approach, you may need to incorporate additional techniques, such as keyword analysis, topic modeling, or machine learning algorithms, to enhance the accuracy of message classification. Message authenticity verification is a complex task that may require advanced methods, including fact-checking and source verification, to ensure its reliability.
Remember to tailor the code to your specific requirements and modify the preprocessing steps, threshold, or incorporate additional techniques as necessary.
Please note that determining the authenticity of a forwarded message is a challenging task and may require more sophisticated methods, including fact-checking, source verification, and considering multiple perspectives.
Read the story on Medium here. Join the Quora community to discuss more this article here.
If you want to share your knowledge, here is the option for you. Use our Guest Post option to submit your post without plagarism. We will publish your content with your name.
 IT2EDU Empowering Education Through Technology
IT2EDU Empowering Education Through Technology